:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/thymus-gland-overview-4582270_FINAL-a4225b38523a4d41bbfaeb4bc6f00226.jpg)
What Is the Thymus Gland and Why Is It Important?
The thymus is a primary lymphoid organ that manifests dynamic physiological changes as animals age in addition to being exquisitely sensitive to stress and toxic insult. It is typically the first lymphoid tissue to respond to immunotoxic xenobiotics, with the first change being loss of cortical lymphocytes by apoptosis.
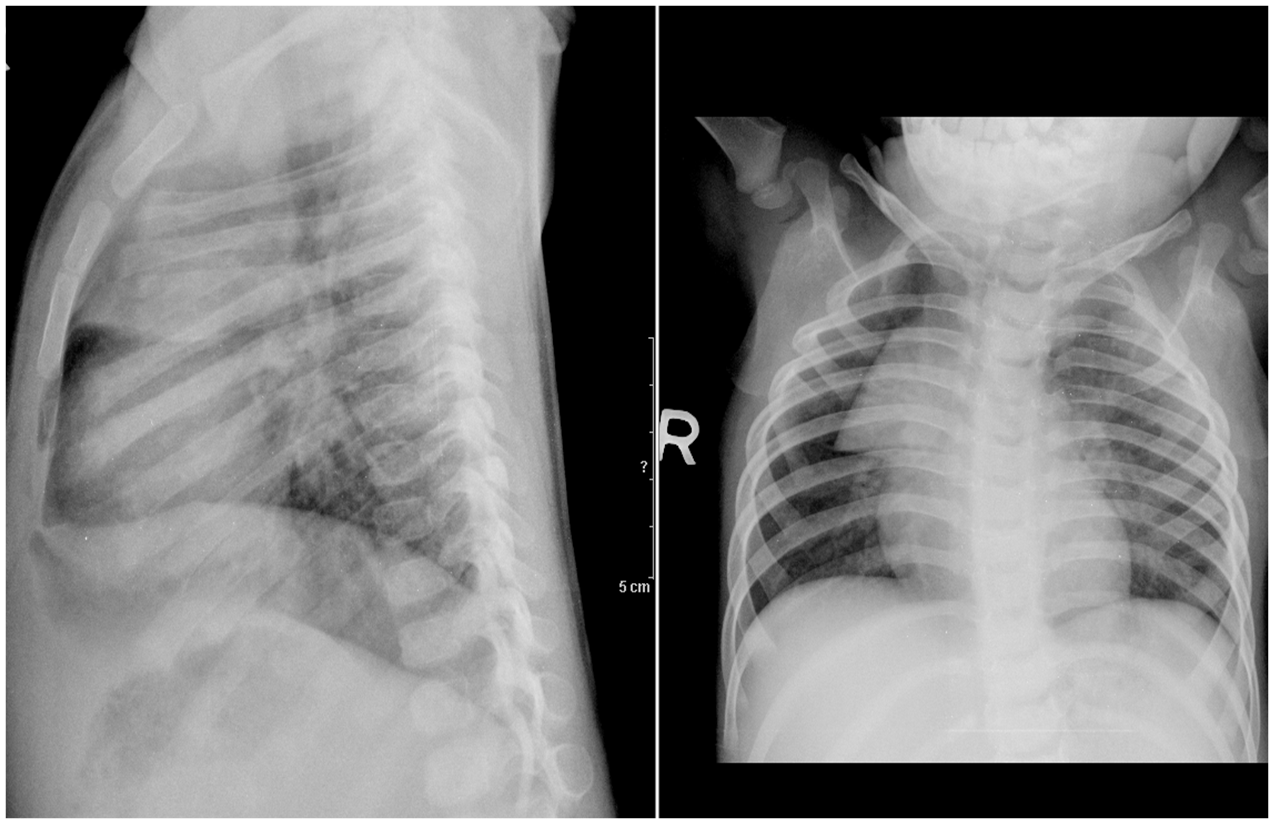
RADIOLOGY IMAGE SPOTTERS Normal thymus
Even though the thymus is exquisitely sensitive to acute insults like infection, shock, or common cancer therapies such as cytoreductive chemo- or radiation-therapy, it also has a remarkable capacity for repair. This phenomenon of endogenous thymic regeneration has been known for longer even than its primary function to generate T cells, however, the underlying mechanisms controlling the.

Thymus rôle, schéma, maladies, cancer, examens
The thymus comprises developing T lymphocytes (thymocytes) as well as cells that support their development, including thymic epithelial cells, other immune cells (B cells, dendritic cells (DCs).
Thymus gland plays critical role in adult health, study finds Tech Explorist
Based on the type, timing and severity of the applied stimulus, stress can exert various actions on the body ranging from alterations in homeostasis to life-threatening effects and death.
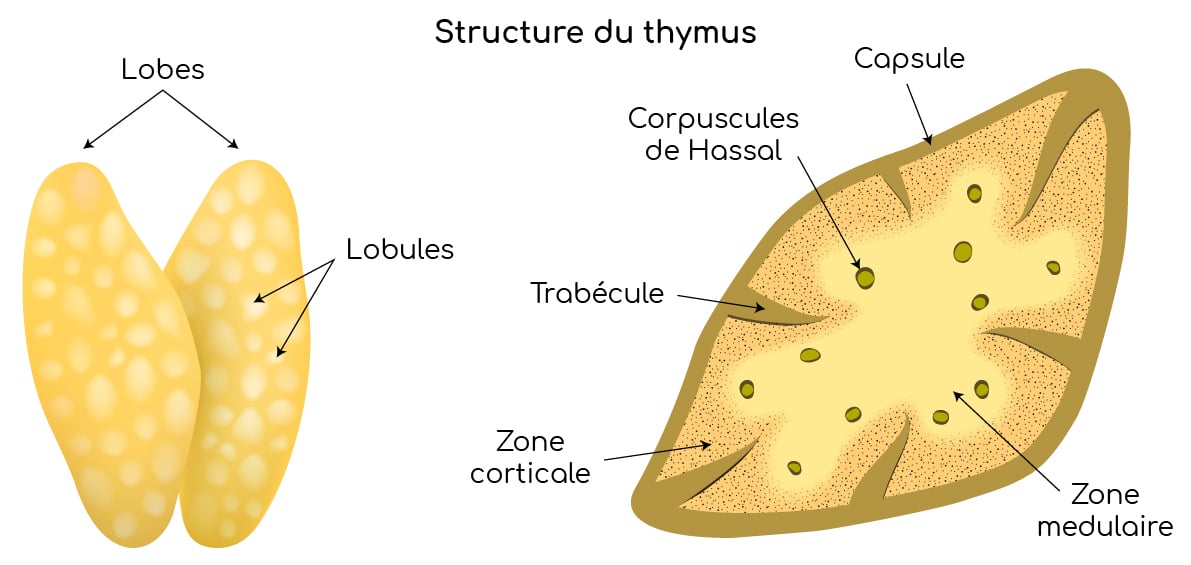
Thymus caractéristiques et fonctions Nutrixeal Info
These therapies have revealed the extreme stress sensitivity of the thymus, but also its remarkable capacity for repair. In a normal setting, thymic function reaches its natural peak during the neonatal and pre-adolescent period, thereafter the thymus begins to decrease in size and activity.. (Wang et al.). While the thymus is usually.
Inflammationdriven deterioration of structural proteins contributes to aging Carnegie
Some of the hallmarks of this thymic response to stress include a reduction in double-positive (DP) thymocytes and reduced output of naïve T cells to the periphery; both of which can.

Struktur des Thymus. Die Thymusdrüse. Infografik, (Lizenzfrei) 566815621
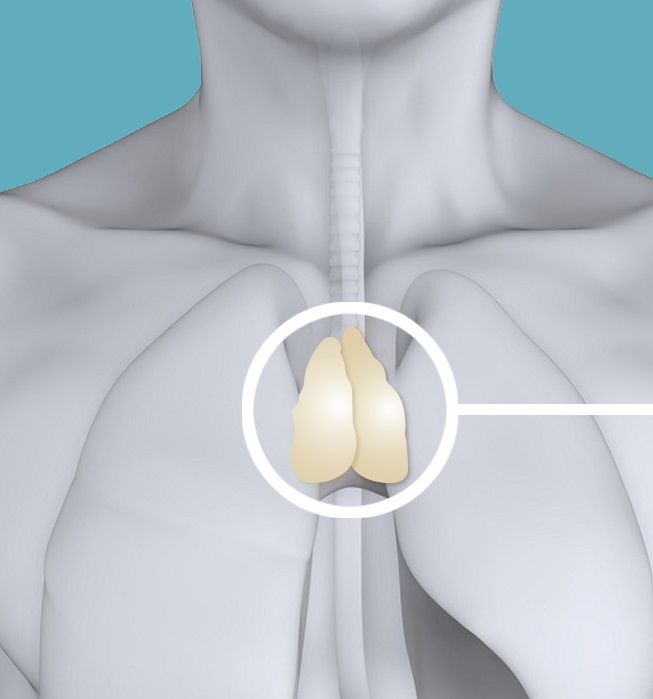
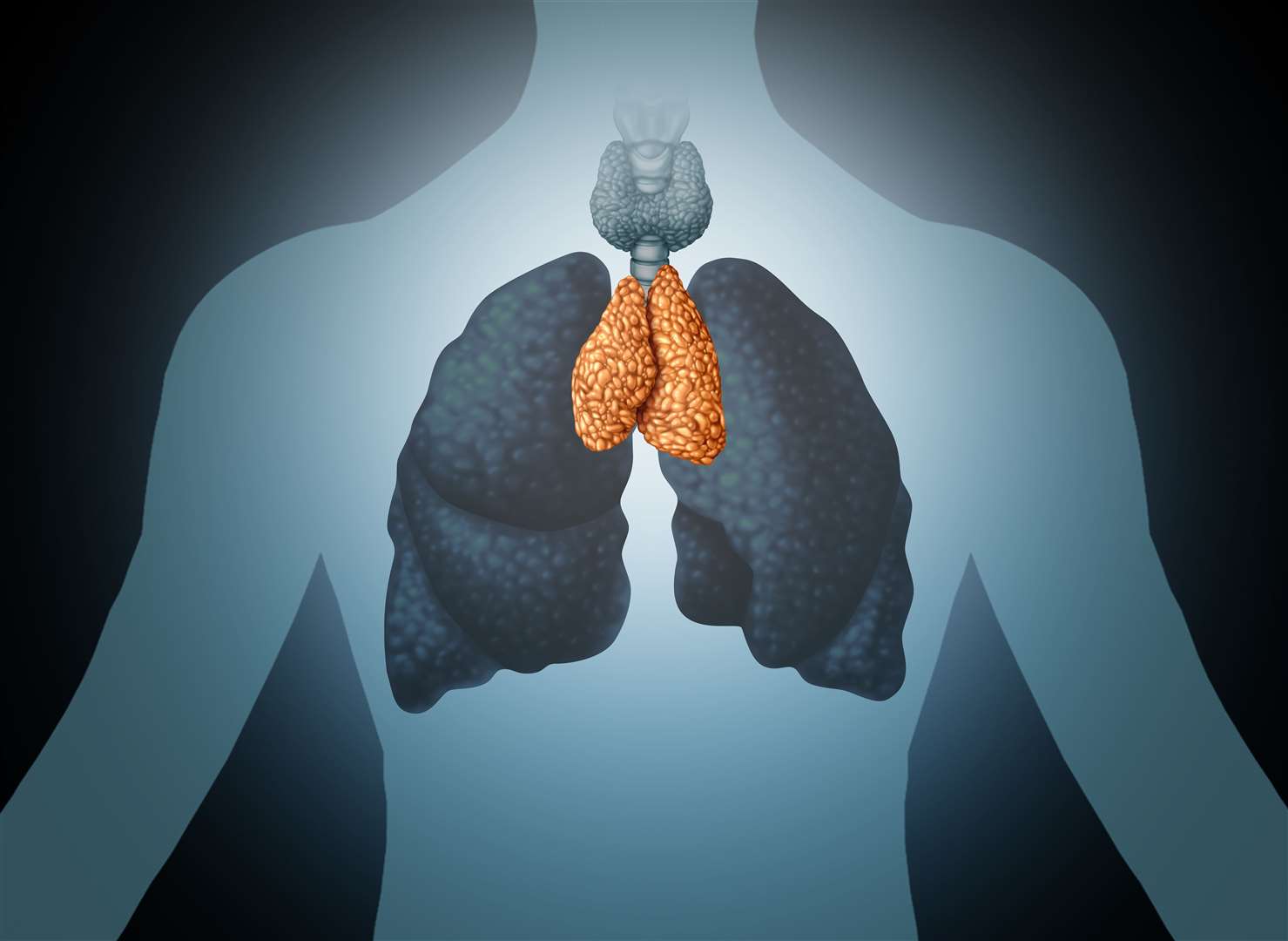
Function Location Types of Thymus Cells Associated Disorders FAQ The thymus gland, located behind the breastbone and between the lungs, plays an important role in developing the immune system. This small organ makes white blood cells, called T-cells, and plays a huge part in training your body to fight infections and cancer cells.

Réflexologie plantaire 7 points d’acupression pour réduire le stress et stimuler le
However, since the thymus is an organ that is sensitive to the effects of stress (endogenous corticosteroids) and aging, it is very important to differentiate chemical-induced thymic atrophy from stress-related lymphocyte apoptosis and age-related thymic involution.

Thymus Tap Modality for Stress Relief and Immune System Boost YouTube
Furthermore, prolactin seems to counteract the immunosupressive effects of glucocorticoids on the thymus under stress conditions,. Chen, Y. K. et al. The frequency and spectrum of thymus 2.

Anatomy, Location, and Functions of the Thymus Facty Health
Given data suggesting that stress affects thymus function, we examined whether blood levels of TRECs might serve as a quantitative peripheral index of cumulative stress exposure and its.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/thymus-tissue-583686076-59fdf9384e4f7d001abb24fb.jpg)
Understanding the Functions of the Thymus
Background Productive thymopoiesis is essential for a robust and healthy immune system. Thymus unfortunately is acutely sensitive to stress resulting in involution and decreased T cell production. Thymic involution is a complication of many clinical settings, including infection, malnutrition, starvation, and irradiation or immunosuppressive therapies. Systemic rises in glucocorticoids and.

Gross anatomy of Thymus Location and Relations in 2021 Gross anatomy, Endocrine system, Anatomy
Stress can affect the thymus by causing a condition called acute thymic atrophy, which can impact the function of the immune system. Many people with thymus problems have no symptoms. Symptoms of thymus problems include reduced resistance to infectious diseases, muscle fatigue, drooping eyelids, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, cough (with bloody sputum), difficulty swallowing.
thymus 快懂百科
Thymocyte interaction with thymic epithelial cells during fetal development establishes a robust and organized environment in which distinct cortical and medullary thymic compartments are formed to provide the architectural framework necessary for thymopoiesis and subsequent export of naïve T cells to the peripheral circulation [ 7 ].
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/human-thymus-anatomy-513000737-d60061aa3a334e67bc64f6177465698c.jpg)
Thymus Location, Function, and Treatment
In humans, monitoring thymus function is typically limited to noninvasive technology, including imaging of thymus size with chest-computed tomography or glucose-analog uptake with positron emission tomography (reviewed in Hudson et al. [9]). Peripheral monitoring of thymus output in humans is restricted to surrogate marker analysis of naïve T.
Fresh hope of new cancer and autoimmune disease therapies as Sanger Institute creates
T-lymphocytes, or T-cells, are one type of white blood cell. In humans, the thymus is an organ you can think as a 'boot camp' for baby T-lymphocytes. It is a place for growth, development, training, and selection of T-lymphocytes, the white-blood-cell immune soldiers, so that they can mature to go out and fight infections and foreign invaders.

Épinglé sur Lheureux Shiatsu
The thymus gland is an important part of your immune system. It helps train the white blood cells that protect your immune system. Fortunately, most of your T-cells were produced before you were even born, and the rest were made during childhood and throughout puberty. Therefore, adults don't really need a thymus.